Introduction: In the digital age, businesses are increasingly reliant on online channels to conduct transactions and engage with customers. Two terms often used interchangeably are “e-commerce” and “digital business.” However, while they share commonalities, they represent distinct approaches to leveraging digital technologies for commercial activities. This article aims to clarify the disparities between e-commerce and digital business, highlighting their definitions, characteristics, and strategic implications for organizations.
Understanding E-Commerce
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet or electronic networks. It involves transactions conducted through online platforms, websites, or digital marketplaces, facilitating exchanges between businesses, consumers, or both. E-commerce encompasses various models, including Business-to-Consumer (B2C), Business-to-Business (B2B), Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C), and more recently, Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) models.
Exploring Digital Business
Digital business encompasses a broader spectrum of activities beyond online transactions, focusing on leveraging digital technologies to transform various aspects of business operations and customer interactions. It involves the integration of digital tools and strategies across marketing, sales, operations, customer service, and beyond. Digital business aims to drive innovation, enhance efficiency, and create value for customers and stakeholders through technology-enabled initiatives.
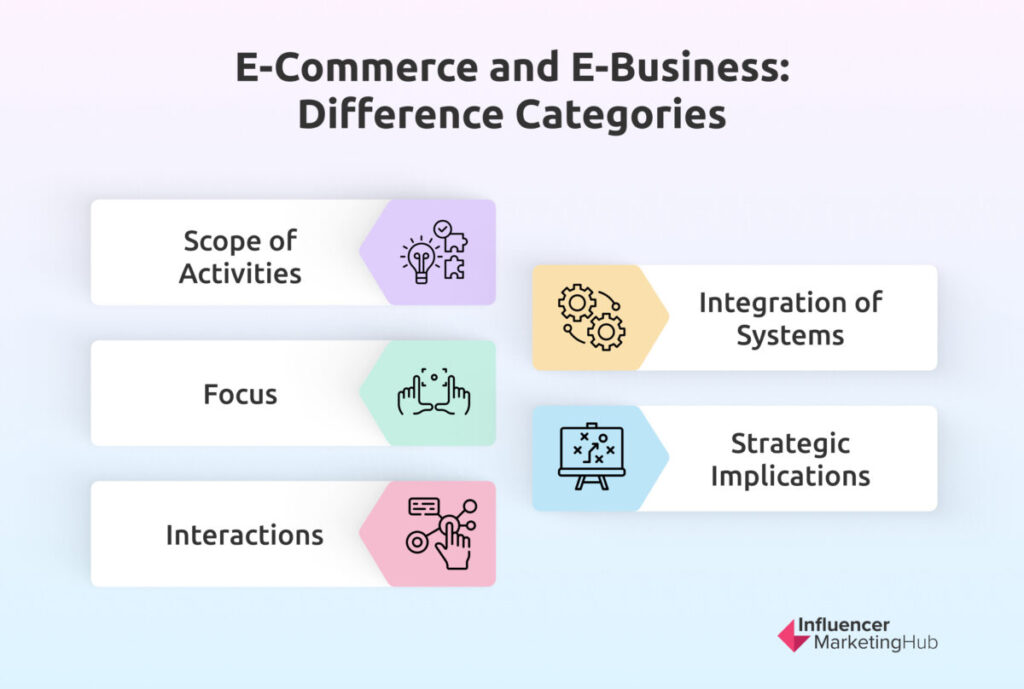
Key Differences
- Transactional vs. Holistic Approach:
- E-commerce primarily revolves around facilitating online transactions, focusing on buying and selling goods and services through digital channels.
- Digital business takes a more holistic approach, integrating digital technologies across all facets of business operations to drive innovation, improve processes, and enhance customer experiences.
- Customer Interaction:
- In e-commerce, customer interaction often revolves around transactional processes, such as browsing products, making purchases, and processing payments.
- Digital business emphasizes building deeper relationships with customers through personalized experiences, data-driven insights, and omnichannel engagement across various touchpoints.
- Scope of Operations:
- E-commerce typically operates within the confines of online transactions, facilitating exchanges through digital platforms or marketplaces.
- Digital business encompasses a broader scope, leveraging digital technologies to transform marketing, sales, supply chain management, customer service, and other aspects of business operations.
- Innovation and Adaptability:
- While e-commerce focuses primarily on facilitating transactions, digital business prioritizes innovation and adaptability, leveraging technology to drive operational efficiencies, explore new business models, and stay ahead of market trends.
Strategic Implications
- Strategic Alignment:
- Organizations need to align their strategies with the nuances of e-commerce and digital business, recognizing the broader implications of digital transformation for their business models and operations.
- Technology Integration:
- Successful digital businesses invest in integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, cloud computing, and IoT across their operations to drive innovation and competitive advantage.
- Customer-Centric Approach:
- Digital businesses prioritize delivering exceptional customer experiences by leveraging data-driven insights, personalization strategies, and seamless omnichannel interactions to meet evolving customer expectations.
- Agility and Flexibility:
- Digital businesses must remain agile and flexible, adapting to changing market dynamics, emerging technologies, and evolving customer preferences to maintain a competitive edge in the digital landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while e-commerce and digital business share commonalities in leveraging digital technologies for commercial activities, they represent distinct paradigms with unique implications for organizations. E-commerce primarily focuses on facilitating online transactions, whereas digital business encompasses a broader spectrum of digital strategies aimed at driving innovation, enhancing efficiency, and delivering superior customer experiences. By understanding the differences between e-commerce and digital business, organizations can develop tailored strategies to capitalize on the opportunities presented by digital transformation and navigate the complexities of the digital landscape effectively.