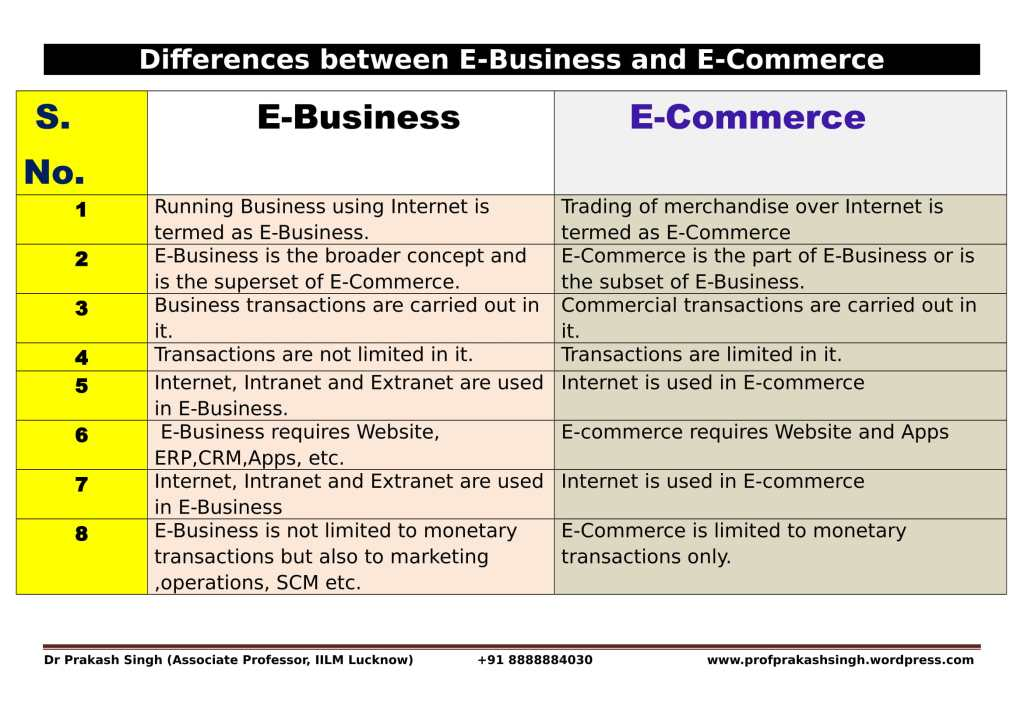
In the realm of online commerce and digital transactions, the terms “e-commerce” and “digital business” are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion regarding their meanings and distinctions. While both concepts involve conducting business activities in the digital realm, they encompass distinct approaches, strategies, and scopes. This article aims to elucidate the difference between e-commerce and digital business, exploring their definitions, characteristics, and implications for modern enterprises.
Understanding E-Commerce
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet or electronic networks. It encompasses transactions conducted through online platforms, websites, or electronic marketplaces, typically involving the exchange of monetary payments for products or services. E-commerce platforms facilitate transactions between businesses (B2B), businesses and consumers (B2C), consumers and consumers (C2C), or even government entities (G2C).
Exploring Digital Business
Digital business, on the other hand, represents a broader concept that encompasses a wide range of digital activities and strategies beyond mere online transactions. While e-commerce focuses primarily on the exchange of goods and services, digital business encompasses a comprehensive approach to leveraging digital technologies to transform various aspects of business operations, including marketing, customer engagement, internal processes, and value creation.
Key Differences
- Scope and Focus:
- E-commerce primarily revolves around online transactions, emphasizing the buying and selling of goods and services through digital channels.
- Digital business encompasses a broader spectrum of activities, including digital marketing, data analytics, customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain optimization, and business model innovation.
- Customer Interaction:
- In e-commerce, customer interaction often revolves around the transactional process, such as browsing products, making purchases, and receiving customer support.
- Digital business emphasizes building deeper and more personalized relationships with customers through digital channels, leveraging data-driven insights to deliver targeted marketing, personalized recommendations, and seamless omnichannel experiences.
- Business Model Innovation:
- While e-commerce platforms primarily focus on facilitating transactions, digital business involves innovating and adapting business models to capitalize on digital technologies and emerging market trends.
- Digital businesses may explore subscription-based models, digital content monetization, platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offerings, and other innovative approaches to generate revenue and create value.
- Integration with Physical Channels:
- E-commerce traditionally operates in the digital realm, with transactions conducted exclusively online.
- Digital business strategies often involve integrating digital and physical channels to create omnichannel experiences, bridging the gap between online and offline interactions to meet customer expectations and preferences seamlessly.
Implications for Modern Enterprises
- Strategic Focus:
- Enterprises must recognize the distinction between e-commerce and digital business and align their strategies accordingly. While e-commerce is essential for online sales, digital business strategies encompass a broader range of digital initiatives aimed at driving growth, innovation, and customer engagement.
- Investment in Technology and Talent:
- Successful digital businesses invest in cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), data analytics, cloud computing, and blockchain, to enhance their digital capabilities and deliver superior customer experiences.
- Building a talented team with expertise in digital marketing, data analysis, user experience (UX) design, and emerging technologies is crucial for executing digital business strategies effectively.
- Adaptability and Innovation:
- Digital businesses must remain agile and adaptable in the face of rapidly evolving digital landscapes, embracing innovation and experimentation to stay ahead of the competition.
- Continuous monitoring of market trends, consumer behavior, and technological advancements is essential for identifying new opportunities and adapting business models accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while e-commerce and digital business share commonalities in their reliance on digital technologies for conducting business activities, they represent distinct concepts with unique scopes, focuses, and implications for modern enterprises. E-commerce primarily revolves around online transactions, whereas digital business encompasses a broader range of digital strategies aimed at transforming various aspects of business operations and customer engagement. Understanding the difference between e-commerce and digital business is crucial for organizations seeking to harness the full potential of digital technologies and thrive in the digital economy. By embracing digital business strategies and leveraging innovative technologies, enterprises can create value, drive growth, and stay competitive in an increasingly digital-centric business landscape.